06. Juli 2016
Like other CMS’s on the market, the Sitecore CMS uses multiple databases that separate stored content. Sitecore content authors should be aware of theses databases and how each affects them.
Let's begin.
After logging into Sitecore, you can access the screen below. If you are not seeing it, change the URL to http://mysiteurlhere>/sitecore/shell. You can view the available databases by selecting the small icon at the bottom right of your screen.

Let’s take a closer look at the databases.
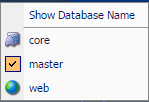
The core database
The core database is where Sitecore stores settings such as users and roles. The Sitecore ribbon configuration is also stored here. This database is where the configuration will be stored if a developer wants to add a new button.
The master database
The master database is where content authors spend their time creating, deleting and editing content. None of these actions affect the live site. In order to change the live site, the content author must publish the item to the web database.
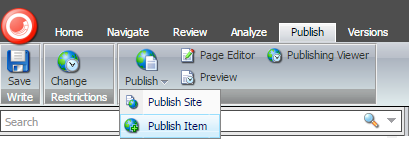
The action of publishing an item will transfer the item to another database – the web database.
The web database
The web database is responsible for the live site. Please be cautious, if you delete a published webpage then the content will be gone instantly.
The preview/staging database
Depending on your website’s build, there may also be a preview or staging database. This preview environment serves as a final test, before the content goes to production. The preview database also allows multiple users to access the website at one time to ensure all the right components have been published correctly before publishing an item (e.g. a full page). This step prevents the website or page from displaying any unexpected behavior once you hit “Publish”.
It is very important for Sitecore content authors to know the differences between these Sitecore CMS databases and to be aware of what database they’re working on at any given moment to avoid content-related mistakes!